Maximum Nominal Voltage for Control Circuits in AC Supply Systems
Regulation 557.3.5.3 states the maximum nominal voltage for control circuits in AC supply systems, specifying different limits for 50 Hz and 60 Hz systems.
OW London Electrician and Home Automation Engineers Team
Maximum Nominal Voltage for Control Circuits in AC Supply Systems
Regulation 557.3.5.3 states:
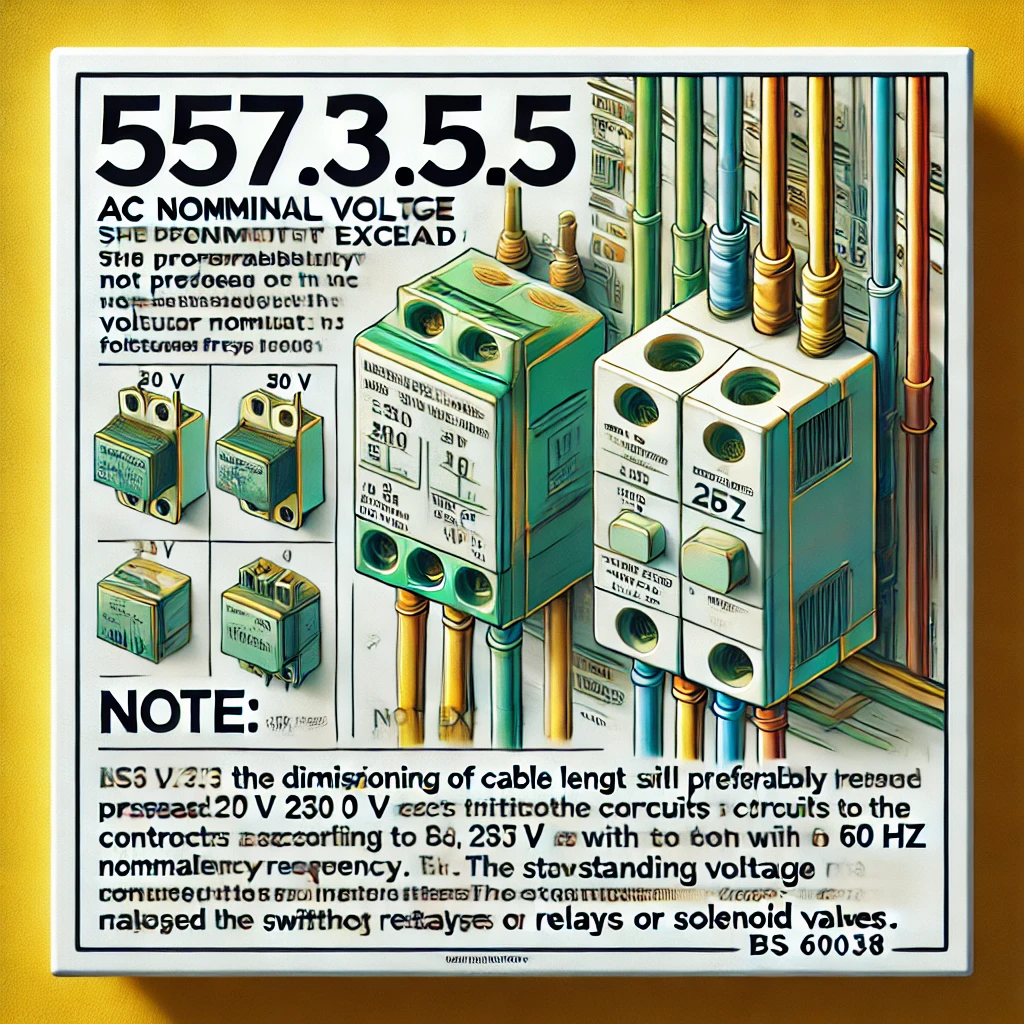
"The nominal voltage of control circuits shall preferably not exceed:
- (i) 230 V for circuits with 50 Hz nominal frequency
- (ii) 277 V for circuits with 60 Hz nominal frequency respectively, taking into account voltage tolerances according to BS EN 60038.
NOTE: The dimensioning of cable length with respect to the conductor capacitances, e.g., connection to a limit switch, needs to be coordinated with the selected relays or solenoid valves. The standing voltage caused by high conductor capacitances may impair the switching off of relays or solenoid valves."
In simple terms, this regulation sets the maximum nominal voltage for control circuits depending on the frequency of the AC supply system. For systems operating at a 50 Hz frequency, the control circuit should not exceed 230 volts. For systems operating at a 60 Hz frequency, the limit is 277 volts. These values help ensure safety and compatibility with standard equipment, considering the typical voltage tolerances as defined by BS EN 60038.

Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Why are there different voltage limits for 50 Hz and 60 Hz systems?
A: The different voltage limits account for the variations in global electrical standards and practices. Most countries using a 50 Hz system standardize at 230 V, while those using a 60 Hz system often standardize at 277 V, aligning with international standards to ensure equipment compatibility and safety.
Q: What is BS EN 60038, and why is it important?
A: BS EN 60038 is a standard that specifies the nominal voltages for low voltage public electricity supply systems. It is important because it provides a common reference for voltage levels, ensuring consistency and safety across different regions and systems.
Q: What does the note about cable length and conductor capacitances mean?
A: The note highlights the importance of considering the capacitance of the cables used in control circuits. High capacitance can cause standing voltage, which might prevent relays or solenoid valves from switching off properly. Therefore, when designing control circuits, it is crucial to match the cable properties with the requirements of the control devices to ensure reliable operation.
What users Saying
Discover what our customers think about our services. Their feedback reflects our commitment to delivering exceptional service and expert solutions for all electrical and security needs.