When can fault protection be omitted for certain equipment according to BS 7671?
Regulation 410.3.9 states The provision for fault protection may be omitted for specific equipment under defined conditions. This regulation outlines several cases where fault protection is not necessary due to the inherent safety of the equipment's design or placement.
OW London Electrician and Home Automation Engineers Team
When can fault protection be omitted for certain equipment according to BS 7671?
Regulation 410.3.9 states:
- "The provision for fault protection may be omitted for the following equipment:
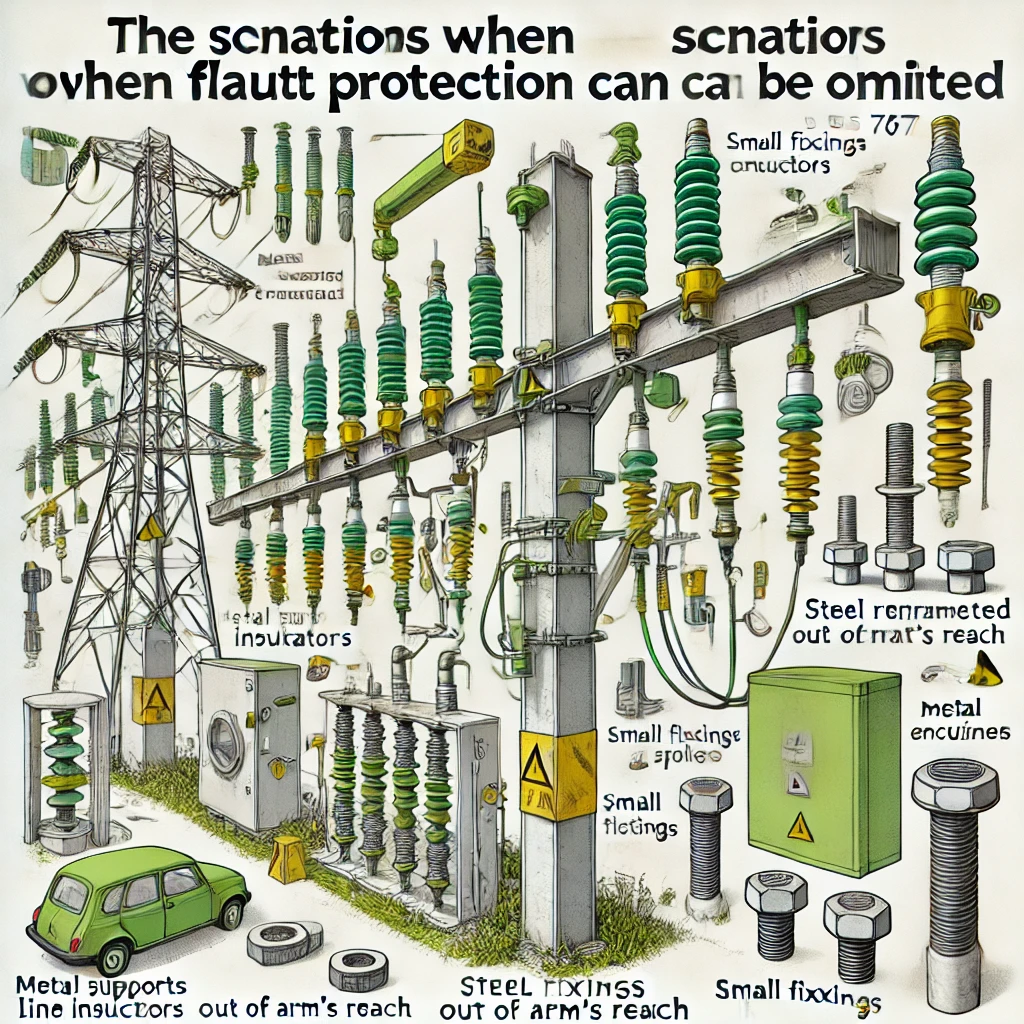
- (i) Metal supports of overhead line insulators which are attached to the building and are placed out of arm’s reach.
- (ii) Steel reinforced concrete poles of overhead lines in which the steel reinforcement is not accessible.
- (iii) Exposed-conductive-parts which, owing to their reduced dimensions (approximate maximum of 50 mm x 50 mm) or their disposition cannot be gripped or come into significant contact with a part of the human body and provided that connection with a protective conductor could only be made with difficulty or would be unreliable.
- NOTE: This exemption applies, for example, to bolts, rivets, nameplates, cable clips, screws, and other fixings.
- (iv) Metal enclosures protecting equipment in accordance with Section 412.
- (v) Unearthed street furniture supplied from an overhead line and inaccessible in normal use."
Fault protection is a safety measure intended to protect people from electric shocks in case of a fault. However, there are certain circumstances where it is deemed safe to omit this protection, as outlined in Regulation 410.3.9. Here’s what this means in simpler terms:
Out of Arm's Reach:
Metal supports of overhead line insulators attached to a building that are placed out of arm's reach do not require fault protection. This is because they are positioned in such a way that a person cannot easily touch them, reducing the risk of electric shock.
Steel Reinforced Concrete Poles:
Concrete poles used in overhead lines that contain steel reinforcement do not need fault protection as long as the steel is not accessible. The concrete acts as a barrier, making it difficult for a person to come into contact with the conductive material.
Small or Inaccessible Conductive Parts:
Exposed-conductive-parts that are either very small (no larger than 50 mm x 50 mm) or positioned in a way that they cannot be easily gripped or touched significantly by a person do not require fault protection. These parts are typically small fixings like bolts, rivets, cable clips, and screws. The difficulty in reliably connecting these parts to a protective conductor makes them exempt.
Metal Enclosures:
Metal enclosures that protect equipment according to specific safety standards (Section 412) are exempt from needing additional fault protection. These enclosures are designed to prevent accidental contact with live parts.
Inaccessible Street Furniture:
Street furniture that is not earthed and is supplied from an overhead line does not need fault protection if it is placed in a location where people cannot normally access it. This ensures that there is minimal risk of electric shock.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is fault protection?
A: Fault protection is a safety measure designed to protect individuals from electric shock in the event of a fault, such as an exposed live wire.
Q: Why are certain equipment exempt from fault protection?
A: Certain equipment is exempt because their design or placement significantly reduces the risk of human contact or makes it impractical to provide effective fault protection. This is detailed in Regulation 410.3.9.
Q: What kind of equipment typically falls under these exemptions?
A: Examples include overhead line insulator supports placed out of reach, steel-reinforced concrete poles, small fixings like bolts and screws, metal enclosures designed to specific standards, and inaccessible street furniture.
Q: What does "out of arm's reach" mean in this context?
A: "Out of arm's reach" means that the equipment is positioned in such a way that a person cannot easily touch it. This significantly reduces the risk of electric shock, making additional fault protection unnecessary.
Q: Are small metal parts like screws and bolts always exempt from fault protection?
A: Yes, provided these parts are small (approximately no larger than 50 mm x 50 mm) or positioned in a way that they cannot be easily gripped or touched significantly. This exemption is mentioned in Regulation 410.3.9.
Q: What safety standards are referred to in Section 412 for metal enclosures?
A: Section 412 refers to specific standards that ensure metal enclosures are designed to prevent accidental contact with live parts, thus eliminating the need for additional fault protection.
What users Saying
Discover what our customers think about our services. Their feedback reflects our commitment to delivering exceptional service and expert solutions for all electrical and security needs.