What is the Minimum Cross-Sectional Area for Protective Conductors in Electrical Installations?
**Regulation 543.1.1 states:** 'The cross-sectional area of every protective conductor, other than a protective bonding conductor, shall be calculated in accordance with Regulation 543.1.3 or selected in accordance with Regulation 543.1.4.'
OW London Electrician and Home Automation Engineers Team
What is the Minimum Cross-Sectional Area for Protective Conductors in Electrical Installations?
Regulation 543.1.1 states:
"The cross-sectional area of every protective conductor, other than a protective bonding conductor, shall be: (i) calculated in accordance with Regulation 543.1.3, or (ii) selected in accordance with Regulation 543.1.4.
Calculation in accordance with Regulation 543.1.3 is necessary if the choice of cross-sectional area has been determined by considerations of short-circuit current and if the earth fault current is expected to be less than the short-circuit current.
If the protective conductor: (iii) is not an integral part of a cable, or (iv) is not formed by conduit, ducting or trunking, or (v) is not contained in an enclosure formed by a wiring system,
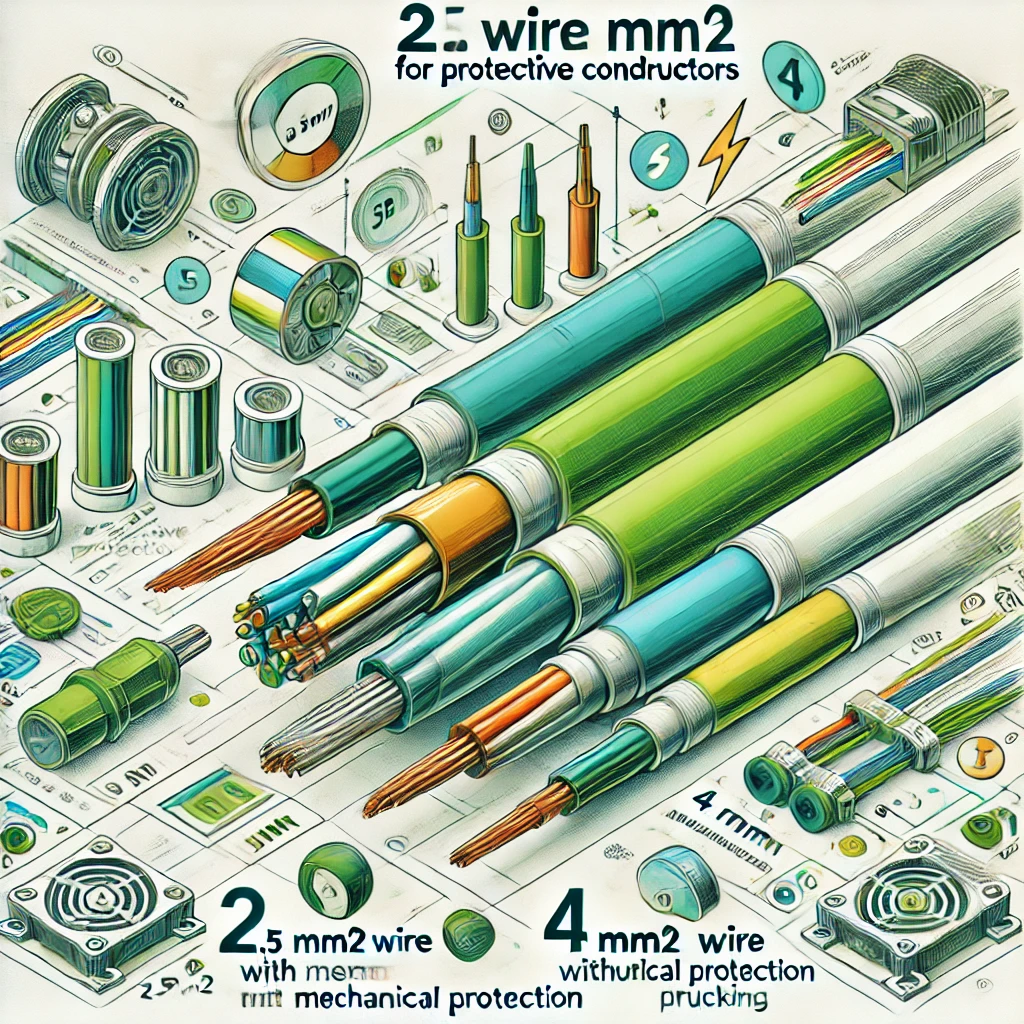
the cross-sectional area shall be not less than 2.5 mm² copper equivalent if protection against mechanical damage is provided, and 4 mm² copper equivalent if mechanical protection is not provided (see also Regulation 543.3.1).
For a protective conductor buried in the ground Regulation 542.3.1 for earthing conductors also applies. The cross-sectional area of a protective bonding conductor shall comply with Section 544."
In electrical installations, protective conductors are essential for safety, ensuring that any fault current is safely conducted to earth. This prevents electric shock and potential fire hazards. Regulation 543.1.1 details the requirements for the cross-sectional area of these conductors.
Calculation Methods: The cross-sectional area of a protective conductor must either be:
- Calculated based on the expected short-circuit current (Regulation 543.1.3), or
- Selected from predefined sizes in another regulation (Regulation 543.1.4).
Minimum Sizes: If the protective conductor is not part of a cable, not within a conduit or trunking, and not inside a wiring enclosure, then specific minimum sizes apply:
- 2.5 mm² if there is mechanical protection (like a conduit or trunking).
- 4 mm² if there is no mechanical protection.
Buried Conductors: If the conductor is buried in the ground, additional rules from Regulation 542.3.1 apply, ensuring it meets requirements for earthing conductors. Protective bonding conductors must follow the guidelines in Section 544.

Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the purpose of a protective conductor?
A: According to Regulation 543.1.1, a protective conductor ensures any electrical fault (like a live wire touching a metal part) is safely conducted to the earth, preventing electric shock and reducing the risk of fire.
Q: Why do protective conductors have different minimum sizes?
A: The sizes vary based on whether the conductor has mechanical protection. Larger conductors (4 mm²) are required if there's no physical protection, providing extra safety against potential damage, as specified in Regulation 543.1.1.
Q: What is mechanical protection in this context?
A: Mechanical protection refers to conduits, trunking, or any physical enclosure that shields the conductor from physical damage, as outlined in Regulation 543.1.1.
Q: When should I use Regulation 543.1.3 for calculation?
A: Use Regulation 543.1.3 when the choice of cross-sectional area depends on the expected short-circuit current, especially if the earth fault current is lower than the short-circuit current.
Q: What are protective bonding conductors?
A: Protective bonding conductors connect parts of an electrical system to the earth, ensuring all metal parts have the same electrical potential, reducing the risk of electric shock, in compliance with Section 544.
What users Saying
Discover what our customers think about our services. Their feedback reflects our commitment to delivering exceptional service and expert solutions for all electrical and security needs.